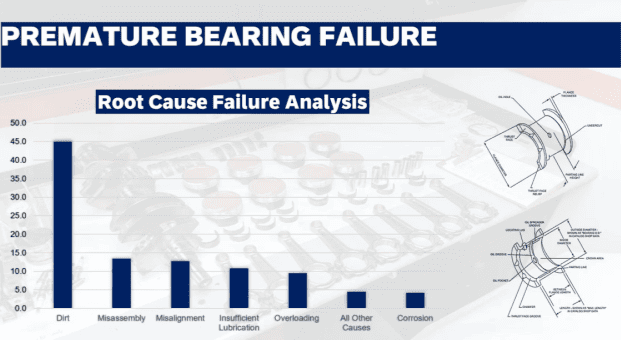
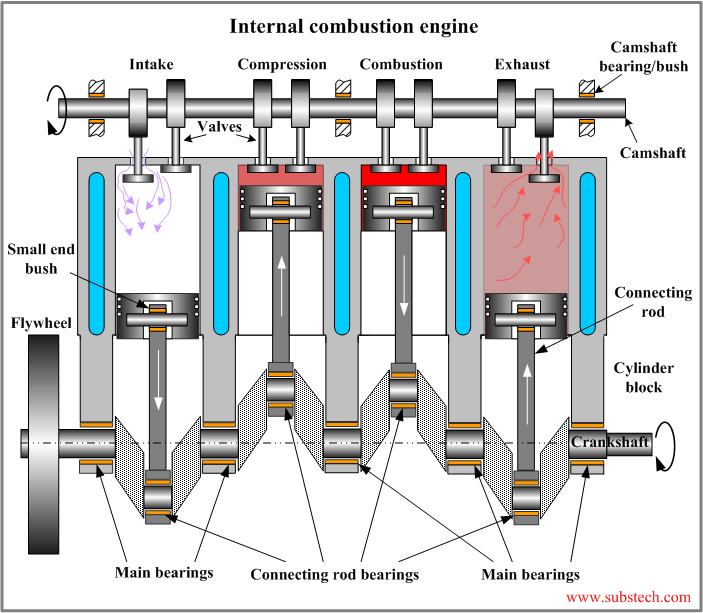
When bearings fail prematurely, it can be a major issue for any engine, leading to costly repairs and downtime. Let's explore the most common causes of bearing failures and how you can prevent them.
Common bearing failures often occur due to poor lubrication, contamination, misalignment, and excessive loads. Identifying these issues early can prevent more significant damage.
Improper maintenance or operating conditions can lead to bearing failure. It’s important to understand the root causes of these failures so you can take steps to prevent them and extend the lifespan of your bearings.
What is the biggest cause of bearing failure?
When we talk about bearing failure, lubrication problems often come to the forefront. If the lubricant is insufficient or contaminated, it cannot perform its primary function of reducing friction and wear. Without proper lubrication, bearings can overheat, leading to metal-to-metal contact and eventual failure.
The biggest cause of bearing failure is inadequate lubrication. Without proper lubrication, bearings experience excessive friction, heat buildup, and eventually wear down prematurely.
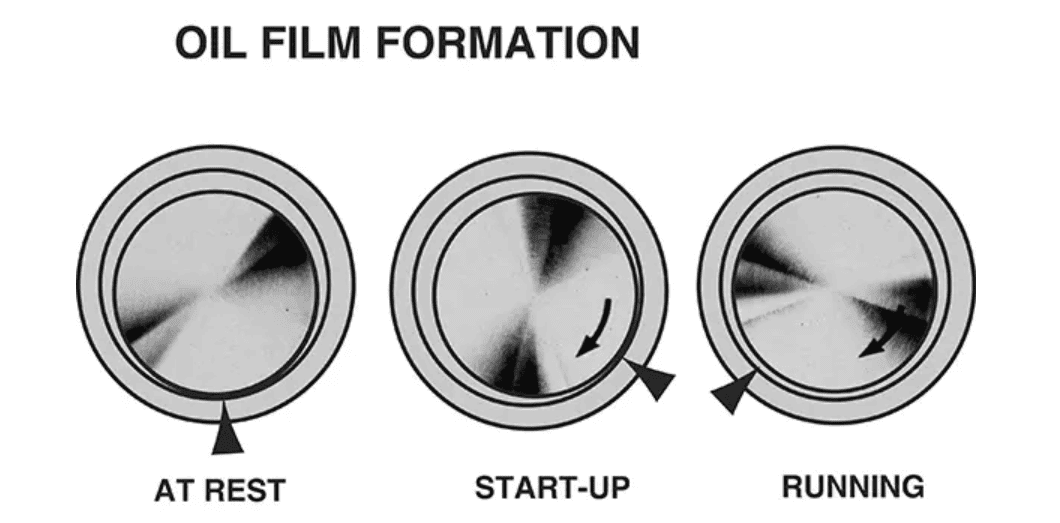
Causes of lubrication failure:
- Inconsistent oil levels: If the oil level is too low, it can’t provide the necessary lubrication.
- Contaminated oil: Dirt or moisture in the oil can lead to premature wear and damage.
- Improper oil type: Using the wrong type of oil can affect the performance of the bearing.
When lubrication fails, the bearing can no longer function properly. Over time, this leads to damage that could have been prevented by regular maintenance and oil checks.
What is the greatest cause of engine bearing wear?
While lubrication is a primary cause, engine bearings can also wear out due to high operating temperatures. When an engine runs too hot, the materials within the bearings expand and can lose their structural integrity. Heat is a common issue for diesel engines, where the temperature can easily exceed optimal levels.
The greatest cause of engine bearing wear is excessive heat. High temperatures can cause the bearing materials to deform, leading to accelerated wear.
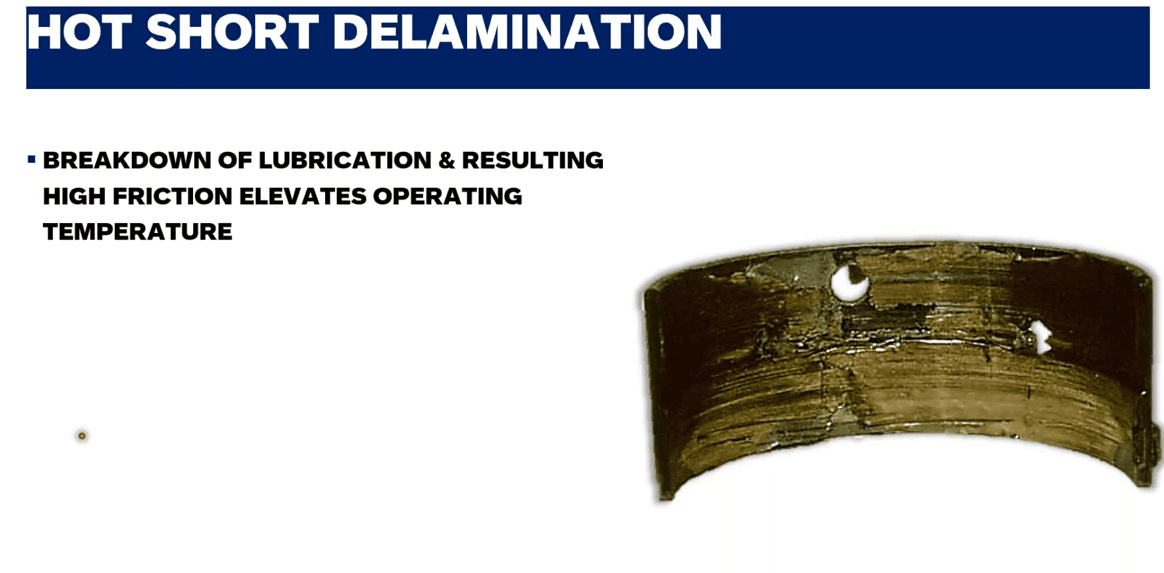
How excessive heat affects engine bearings:
- Deformation of bearing materials: High temperatures can cause metal bearings to deform, reducing their ability to function.
- Oil breakdown: Excessive heat can degrade the oil, rendering it ineffective at lubricating the bearings.
- Increased wear: Overheated bearings wear down much faster than those running at normal temperatures.
The combination of heat and poor lubrication can lead to catastrophic bearing failure if not addressed.
Why do my bearings keep failing?
If your bearings keep failing, there could be a combination of issues at play. Apart from lubrication and heat, factors like contamination, misalignment, and overloading can contribute to bearing failure. Bearings are delicate components, and any irregularities in their working conditions can significantly shorten their lifespan.
Your bearings might keep failing due to a combination of poor lubrication, contamination, misalignment, or excessive load on the bearings. Identifying the root cause is key.
Diagnosing the root cause:
- Poor lubrication: Check oil levels and quality regularly.
- Contamination: Ensure clean operating conditions to prevent debris from entering the bearings.
- Misalignment: Make sure the bearings are properly installed and aligned with other components.
- Overloading: Make sure your bearings are rated for the specific loads they're subjected to.
Each of these factors can cause repetitive bearing failure. Regular maintenance, proper installation, and operating within recommended limits can help prevent these issues.
Conclusion
Inadequate lubrication, excessive heat, contamination, misalignment, and overload are common causes of bearing failure. Regular maintenance is the key to extending the lifespan of your bearings.